KEY EXPERIENCE
The sys admin's daily grind: Single-packet authentication
ByConventional, woodpecker-style port knocking is open to sniffing and brute force knocking attacks. Sending an encrypted packet with an access request to the server is safer and more modern. Learn more about Firewall Knock Operator, a.k.a. Fwknop.
Conventional port knocking, which I described last month, protects you against attackers who routinely scan whole networks looking for "low-hanging fruit." A cracker who takes more time and logs communications can also identify knocking signals because the sequences will repeat.
In theory, you might consider using lists of one-off knocking signals that become obsolete after use. Unfortunately, this is really complex. Besides, if the administrator is not creative enough, an attacker could just try out popular knocking sequences (port 7000, 8000, 9000, ?) to gain access.
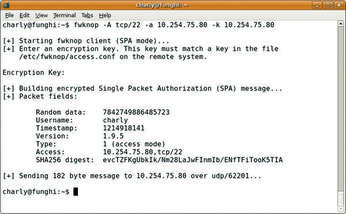 Figure 1: The client knocking on the door of port 22 is allowed to pass because it possesses the right key.
Figure 1: The client knocking on the door of port 22 is allowed to pass because it possesses the right key.
Single-Packet Authentication (SPA) is one possible solution. The knocking system sends a single packet containing the encrypted authentication credentials – typically a pass phrase – and the client request to open a specific port. An SPA implementation that works really well is Firewall Knock Operator, or Fwknop [2]. Besides the normal build tools, the installation requires Perl, the libpcap-dev package, and the CPAN Net::Pcap module. After installing all of these resources, installing Fwknop is a breeze thanks to the Perl-based installer.
Matching Knobs
Fwknop comprises the fwknopd server and the fwknop client. By editing two files below /etc/fwknop/, you can configure the server; fwknop.conf contains the basic configuration. Initially, you will just need to change a couple of parameters, which are tagged __CHANGEME__.
The other knobs you could tweak here have very sensible defaults. Note that you need to synchronize the time between the server and the client because if the difference is too big, fwknopd will ignore the knocking client.
The entries in /etc/fwknop/access.conf define how fwknopd responds to a client knocking. The secret key that the client uses to identify itself is stored here. The SOURCE line can be used to restrict the networks from which the daemon accepts knocking. To set the port that the system opens on successful knocking – for example, tcp/22 for SSH – you can use OPEN_PORTS. Figure 1 shows a successful attempt. The fwknop client picks up the key from its own /etc/fwknop/access.conf.
If the SSH connection doesn't open quickly enough, the FW_ACCESS_TIMEOUT on the server triggers. This time is normally set to 30 seconds, but I went for twice that – never rush an admin on the job!
INFO
[1] "Knock-Knock" by Charly Kühnast, Linux Magazine, September 2008,
[2] Fwknop: http://www.cipherdyne.org/fwknop
Charly Kühnast is a Unix operating system administrator at the Data Center in Moers, Germany. His tasks include firewall and DMZ security and availability. He divides his leisure time into hot, wet, and eastern sectors, where he enjoys cooking, fresh water aquariums, and learning Japanese, respectively.
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Bugs Found in sudo
Two critical flaws allow users to gain access to root privileges.
-
Fedora Continues 32-Bit Support
In a move that should come as a relief to some portions of the Linux community, Fedora will continue supporting 32-bit architecture.
-
Linux Kernel 6.17 Drops bcachefs
After a clash over some late fixes and disagreements between bcachefs's lead developer and Linus Torvalds, bachefs is out.
-
ONLYOFFICE v9 Embraces AI
Like nearly all office suites on the market (except LibreOffice), ONLYOFFICE has decided to go the AI route.
-
Two Local Privilege Escalation Flaws Discovered in Linux
Qualys researchers have discovered two local privilege escalation vulnerabilities that allow hackers to gain root privileges on major Linux distributions.
-
New TUXEDO InfinityBook Pro Powered by AMD Ryzen AI 300
The TUXEDO InfinityBook Pro 14 Gen10 offers serious power that is ready for your business, development, or entertainment needs.
-
LibreOffice Tested as Possible MS Office Alternative
Another major organization has decided to test the possibility of migrating from Microsoft Office to LibreOffice.
-
Linux Mint 20 Reaches EOL
With Linux Mint 20 at its end of life, the time has arrived to upgrade to Linux Mint 22.
-
TuxCare Announces Support for AlmaLinux 9.2
Thanks to TuxCare, AlmaLinux 9.2 (and soon version 9.6) now enjoys years of ongoing patching and compliance.
-
Go-Based Botnet Attacking IoT Devices
Using an SSH credential brute-force attack, the Go-based PumaBot is exploiting IoT devices everywhere.
