Perl script sets up Jenkins jobs to automate builds and tests
Automatic Testing

Instead of configuring the Jenkins continuous integration server in the browser with mouse clicks and text input for builds, programmers can store the necessary data in the source control system and let a Perl script do the work.
Continuous integration (CI) and the associated productivity gains are now firm favorites in the development universe. Input the code into the source control system, issue a pull request, have a co-worker check it – already the cogwheels of the CI pipeline grab the change, run it through the ever-growing test suite, and, presto, everything gets released all at once. CI servers like Jenkins [1] or TeamCity [2], which grab the latest source versions of a project and fire up a build with all tests and possible deployment steps, are enjoying growing popularity.
But spending two minutes creating a new build project in Jenkins' recalcitrant interface can wear down the enthusiasm of even the most motivated developers. As Figure 1 shows, the quest here is to find the required boxes, check them, and fill out some text fields.
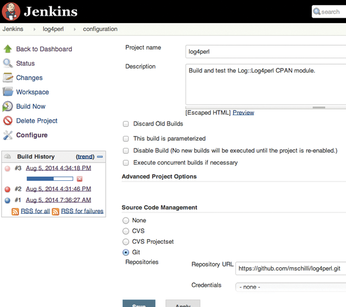 Figure 1: Jenkins is currently performing a build and test of the CPAN log4perl project, which resides on GitHub.
Figure 1: Jenkins is currently performing a build and test of the CPAN log4perl project, which resides on GitHub.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.
-
Linux Mint 22.3 Now Available with New Tools
Linux Mint 22.3 has been released with a pair of new tools for system admins and some pretty cool new features.
-
New Linux Malware Targets Cloud-Based Linux Installations
VoidLink, a new Linux malware, should be of real concern because of its stealth and customization.
-
Say Goodbye to Middle-Mouse Paste
Both Gnome and Firefox have proposed getting rid of a long-time favorite Linux feature.
-
Manjaro 26.0 Primary Desktop Environments Default to Wayland
If you want to stick with X.Org, you'll be limited to the desktop environments you can choose.
-
Mozilla Plans to AI-ify Firefox
With a new CEO in control, Mozilla is doubling down on a strategy of trust, all the while leaning into AI.

