Program in the cloud with GitHub Codespaces
Out in Space

© Lead Image © Noel Powell, Fotolia.com
Imagine you want to build a program from the source code and discover that your distribution lacks the tool and software package versions you need to do so. Instead of using your own virtual machine, you can now switch to GitHub Codespaces.
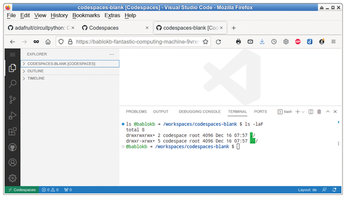
In simple terms, Codespaces consists of a Docker container with a Linux system and the Visual Studio Code (VSC) editor as the sole user interface (Figure 1). As VSC has an integrated terminal, it also has a command line. And thanks to root access, you can use it to install arbitrary software.
A codespace provides computing power (CPUs) and memory. Of course, the operator, in this case Microsoft as the owner of GitHub, asks you to pay for this. The free starter offer consists of 120 CPU hours and 15GB of disk space per month. Because the smallest system comes with two CPUs, you actually have 60 hours of computing time at your disposal. This is enough for about two hours of programming per day.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
OpenMandriva Lx 6.0 Available for Installation
The latest release of OpenMandriva has arrived with a new kernel, an updated Plasma desktop, and a server edition.
-
TrueNAS 25.04 Arrives with Thousands of Changes
One of the most popular Linux-based NAS solutions has rolled out the latest edition, based on Ubuntu 25.04.
-
Fedora 42 Available with Two New Spins
The latest release from the Fedora Project includes the usual updates, a new kernel, an official KDE Plasma spin, and a new System76 spin.
-
So Long, ArcoLinux
The ArcoLinux distribution is the latest Linux distribution to shut down.
-
What Open Source Pros Look for in a Job Role
Learn what professionals in technical and non-technical roles say is most important when seeking a new position.
-
Asahi Linux Runs into Issues with M4 Support
Due to Apple Silicon changes, the Asahi Linux project is at odds with adding support for the M4 chips.
-
Plasma 6.3.4 Now Available
Although not a major release, Plasma 6.3.4 does fix some bugs and offer a subtle change for the Plasma sidebar.
-
Linux Kernel 6.15 First Release Candidate Now Available
Linux Torvalds has announced that the release candidate for the final release of the Linux 6.15 series is now available.
-
Akamai Will Host kernel.org
The organization dedicated to cloud-based solutions has agreed to host kernel.org to deliver long-term stability for the development team.
-
Linux Kernel 6.14 Released
The latest Linux kernel has arrived with extra Rust support and more.