Migrating from CentOS 7
ELevate to the Future

© Lead Image © sergeyback, 123RF.com
CentOS 7 reaches end of life in June 2024, forcing users to look for a free enterprise Linux alternative. AlmaLinux's ELevate migration tool can help ease the transition.
For years, CentOS was the operating system of choice for users who needed a free enterprise Linux solution. CentOS offered a predictable life cycle and a long lifespan for each release, making it a reliable alternative to the commercial Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) distribution. That all changed in 2020 when Red Hat replaced CentOS 8 with CentOS Stream and announced that CentOS 7 would reach end of life on June 30, 2024.
Despite its name, CentOS Stream does not serve as a replacement for CentOS. While CentOS sat downstream of RHEL, making it a reliable replacement for RHEL, CentOS Stream sits upstream and serves as a developmental platform for RHEL contributors. As a result, Red Hat has warned that CentOS Stream is not considered stable for production environments [1].
As one would expect from the open source community, CentOS alternatives started popping up almost immediately after this announcement. One of these alternatives, AlmaLinux [2], quickly stepped in as a replacement for CentOS by offering 1:1 bug compatibility with RHEL by early 2021, eventually moving to application binary interface compatibility in 2023 when Red Hat restricted access to RHEL source code. Today, AlmaLinux provides an alternative for former CentOS users as a forever-free, community-governed, production-grade platform focused on long-term stability.
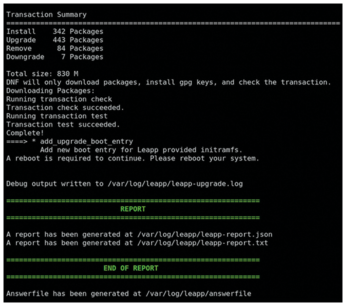
While an alternative free enterprise Linux solution like AlmaLinux is good news in light of the fast approaching CentOS end of life, administrators still need to migrate their existing CentOS systems to a new enterprise Linux distribution. Migration isn't exactly a trivial task. Luckily, AlmaLinux has an answer for this migration problem: ELevate [3]. By combining Red Hat's Leapp [4] framework with a community-created migration metadata library and service, ELevate lets you convert an existing CentOS 7.x install to the 8.x version of a RHEL derivative. Developed by AlmaLinux to be agnostic, ELevate supports upgrade paths for multiple RHEL derivatives (see Figure 1). You can also use ELevate as a regular upgrade tool.
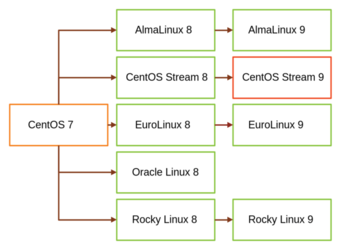 Figure 1: AlmaLinux supports multiple upgrade paths. Notice that ELevate does not support upgrading from Oracle Linux 8 to Oracle Linux 9. Upgrading to CentOS Stream 9 is still experimental at the time of writing.
Figure 1: AlmaLinux supports multiple upgrade paths. Notice that ELevate does not support upgrading from Oracle Linux 8 to Oracle Linux 9. Upgrading to CentOS Stream 9 is still experimental at the time of writing.
Until recently, ELevate only supported official operating system repositories. If your CentOS install used "extra" repositories, such as the popular Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository, you could only migrate using ELevate Testing. ELevate now offers third-party EPEL support for migrating from CentOS 7 to AlmaLinux 8 in the stable release [5]. Furthermore, ELevate has added support for other repositories (Imunify, KernelCare, MariaDB, NGINX, and PostgreSQL) for all supported systems (AlmaLinux, CentOS, EuroLinux, Oracle Linux, and Rocky Linux).
With CentOS 7's end of life quickly approaching, system administrators need to develop a migration plan. AlmaLinux's ELevate tool can help ease the pain of migration. In this article I will show you how to use ELevate to migrate from CentOS 7 to AlmaLinux 8.
Precautions Before Upgrading
This article intends to be a quickstart guide on ELevate to help you upgrade away from CentOS 7 to AlmaLinux quickly and painlessly. Before you get started, it is important you adopt the necessary precautions and make the required preparations.
While ELevate is being used to upgrade production systems in the wild, caution is still advised. At the very least, you should back up your systems before you get started, just in case. AlmaLinux recommends doing a trial run in a sandbox to verify the migration works in your environment before migrating a production system.
The upgrade process will be done in-place, which means AlmaLinux will be installed over your CentOS instance directly. The machine being subjected to conversion will need to be rebooted more than once.
Only single-step upgrades are supported. This means that if you intend to migrate to AlmaLinux 9, you will need to migrate to AlmaLinux 8 first and then upgrade from there.
Gathering the Tools
Before you start migrating, you first must ensure your CentOS instance is up to date. I like to reboot after system updates to ensure every installed service loads the updated components as follows:
$ sudo yum update -y $ sudo reboot
Next, you need to install ELevate. You can install the standard release from the associated AlmaLinux repository, which you can enable as follows:
$ sudo yum install -y http://repo.almalinux.org/elevate/elevate-release-latest-el$(rpm --eval %rhel).noarch.rpm
As mentioned earlier, ELevate uses Red Hat's upgrade tool, Leapp. In order to migrate to AlmaLinux, you must fetch Leapp, along with the patch files that will configure it to upgrade CentOS 7 into AlmaLinux:
$ sudo yum install -y leapp-upgrade leapp-data-almalinux
Ready to Migrate
It is a good idea to ensure your applications will run on AlmaLinux before you migrate. AlmaLinux provides a pre-upgrade check to determine the feasibility of the migration. When migrating from CentOS 7, you are likely to get a failure message at this stage, which is to be expected (Figure 2). Make sure you invoke the preupgrade checks with the following command:
$ sudo leapp preupgrade
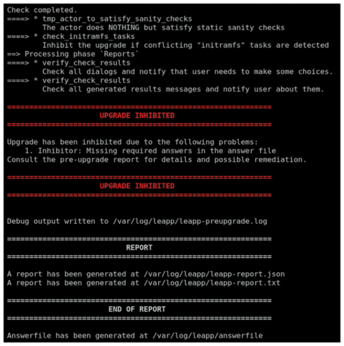 Figure 2: This failure message is to be expected. In order to proceed further, you need to fix the problems listed in /var/log/leapp/answerfile.
Figure 2: This failure message is to be expected. In order to proceed further, you need to fix the problems listed in /var/log/leapp/answerfile.
During the pre-upgrade stage, a report will be saved to /var/log/leapp/leapp-report.txt with a list of dangerous actions that might occur during the migration. Some suggestions are also given. Most likely, a file will be generated in /var/log/leapp/answerfile with questions that require a true/false answer. These questions must be answered before the upgrade can take place (Figure 3). You can answer these questions by either editing the file directly or using leapp answer. Listing 1 shows the bare minimum fixes you should perform immediately after running preupgrade in order to satisfy the answerfile from a CentOS 7 install.
Listing 1
Common Fixes after the Pre-Upgrade
01 sudo rmmod pata_acpi 02 echo PermitRootLogin yes | sudo tee -a /etc/ssh/sshd_config 03 sudo leapp answer --section remove_pam_pkcs11_module_check.confirm=True
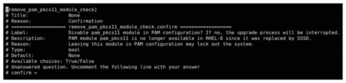 Figure 3: The issues listed in /var/log/leapp/answerfile must be resolved before the upgrade process can commence.
Figure 3: The issues listed in /var/log/leapp/answerfile must be resolved before the upgrade process can commence.
Once you are ready, launch the upgrade by issuing the final command:
$ sudo leapp upgrade
You will need to reboot manually afterwards (Figure 4). The machine will boot into your new AlmaLinux 8 distribution. If you run into any additional issues, please see the ELevate Frequent Issues page on the AlmaLinux website [6].
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
OpenMandriva Lx 6.0 Available for Installation
The latest release of OpenMandriva has arrived with a new kernel, an updated Plasma desktop, and a server edition.
-
TrueNAS 25.04 Arrives with Thousands of Changes
One of the most popular Linux-based NAS solutions has rolled out the latest edition, based on Ubuntu 25.04.
-
Fedora 42 Available with Two New Spins
The latest release from the Fedora Project includes the usual updates, a new kernel, an official KDE Plasma spin, and a new System76 spin.
-
So Long, ArcoLinux
The ArcoLinux distribution is the latest Linux distribution to shut down.
-
What Open Source Pros Look for in a Job Role
Learn what professionals in technical and non-technical roles say is most important when seeking a new position.
-
Asahi Linux Runs into Issues with M4 Support
Due to Apple Silicon changes, the Asahi Linux project is at odds with adding support for the M4 chips.
-
Plasma 6.3.4 Now Available
Although not a major release, Plasma 6.3.4 does fix some bugs and offer a subtle change for the Plasma sidebar.
-
Linux Kernel 6.15 First Release Candidate Now Available
Linux Torvalds has announced that the release candidate for the final release of the Linux 6.15 series is now available.
-
Akamai Will Host kernel.org
The organization dedicated to cloud-based solutions has agreed to host kernel.org to deliver long-term stability for the development team.
-
Linux Kernel 6.14 Released
The latest Linux kernel has arrived with extra Rust support and more.