Not So Brave New World
A for-profit, open source browser
ByThe Brave browser promises speed and privacy, but its quest for profit compromises security at every turn.
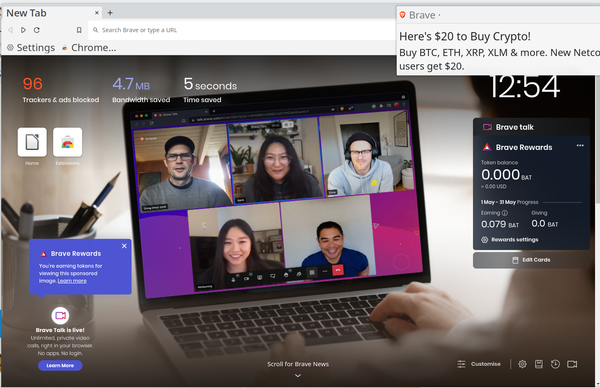
I had thought that for-profit web browsers had died with the 20th century. Long since, I imagined, the web browser had become such an essential part of modern computing that there was no profit left in it. Brave Software, however, disagrees. Since 2016, the company has been developing its open source browser (Figure 1), attempting to fund it with a restricted marketplace for ads – an idea compelling enough to convince venture capitalists to invest over seven million dollars. However, those with minimal knowledge of privacy and security are likely to think otherwise. Based on Chromium and compatible with Chrome extensions, the Brave browser itself is functional enough, with an array of tools designed to appeal to modern users, especially those who want to dabble in cryptocurrencies. Yet again and again, Brave reveals itself as a battleground where privacy and security are at odds with the quest for profit.
Brave has official packages for Debian, Fedora, and openSUSE, optimized for releases that are a couple of years old, but which should still work. Snap packages are also available, although the download page warns that they are less polished. Community built packages are also available for Arch, Manjaro, Solus, and Flatpak. Regardless of how you install, Brave opens on a dashboard that has to be bypassed by clicking on the Home button before you can begin to browse.
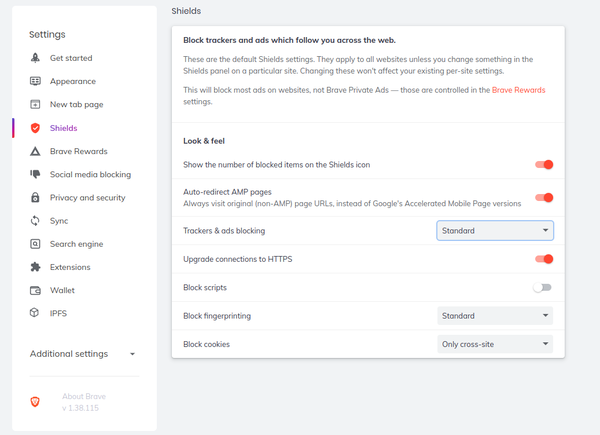
However, before you browse, you will probably want to click the Settings tab to customize the browser (Figure 2). The tab includes the usual appearance choices, as well as settings for a cryptocurrency wallet, a secure search engine, Chrome extensions, and peer-to-peer networking. At the bottom is a grab bag of settings that includes autofill for passwords, payment methods and addresses, download directories, and hardware interaction. Overall, the Settings tab is a mixture of the ordinary and trendy that is convenient but not outstanding. You could get most of these settings from extensions, although installing them would take more time. The same is true of other features, such as the built-in QR code reader.
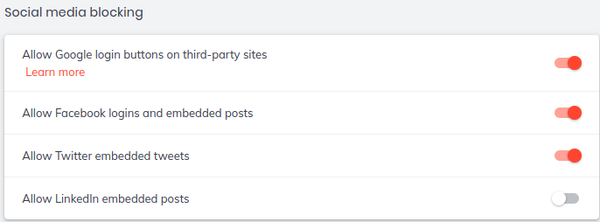
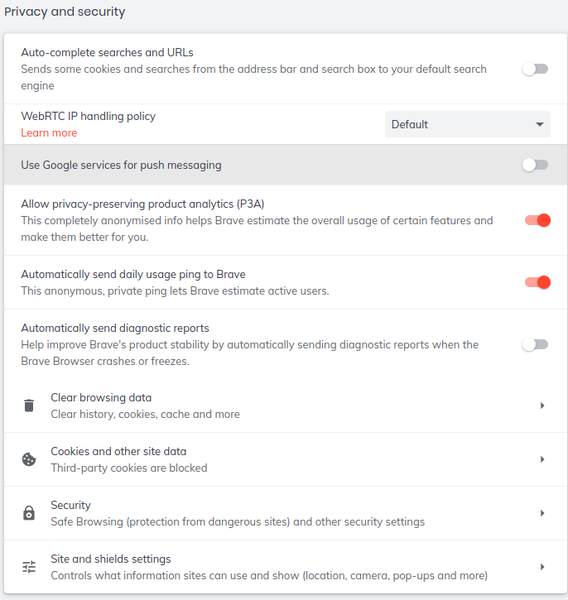
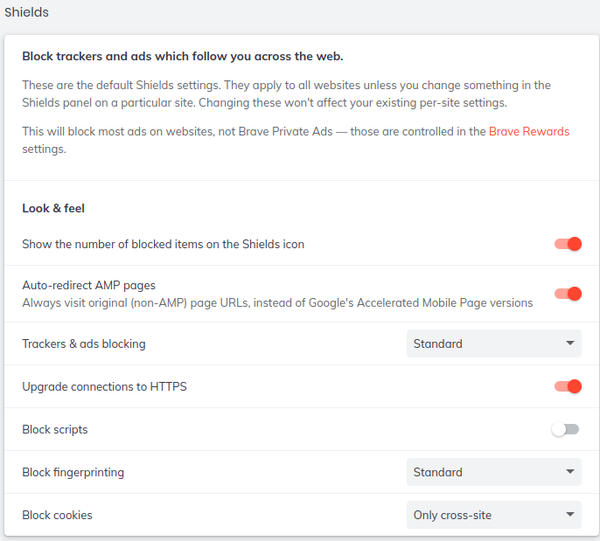
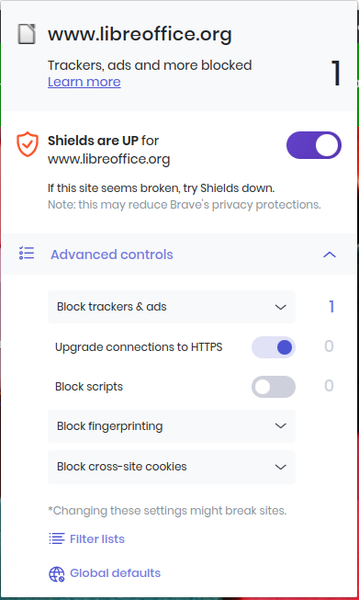
Almost lost among the other settings are those for privacy and security. Brave allows you to block social media sites in whole or in part (Figure 3). In addition, under Privacy and security are settings to clear browsing data, block cookies, and warn of potentially dangerous sites (Figure 4). The important settings are under Shields, which has settings for blocking trackers and ads, scripts, fingerprinting, and cookies (Figure 5). Together, these settings give moderate protection, but most can be turned off or – if you are feeling rash – relaxed altogether. When you are browsing, each page’s settings can also be set individually (Figure 6). When added to the anonymous browsing provided by the Tor Browser, Brave offers a comprehensive set of privacy and security settings.
A Conflict Between Privacy and Profit
Unfortunately, Brave’s privacy and security settings are only half the story. If I sound hesitant about Brave, that is because Brave’s attempt to combine profit with privacy and security often appears to be a contradiction. To start with, the home page claims that it lets users browse “up to 6x faster,” and the browser even keeps track of the time that it has supposedly saved you. Yet even allowing for the ambiguity of “up to,” this statement is wide off the mark. On my system, Brave opens and refreshes pages sluggishly, which is only to be expected when the Tor Browser is rerouting through onion sites. Similarly, although Brave is faster to begin downloads than Chromium or Firefox, if anything, its download speed seems fractionally slower than either. True, the speed is increased if Tor Browser is turned off, but it seems the marketing claim of greater speed is hard to reconcile with the claim of “a safer Internet.” After a day of use in preparation for this review, even Brave itself only claimed to have saved me five seconds.
More significantly, while advertising privacy, Brave is set by default to collect data about how you use features, your daily usage, and diagnostic reports of any freezes or crashes. This information is supposed to be anonymous and can be turned off, but it is inconsistent with an emphasis on privacy. If it must be collected, at the very least, users should have the chance to allow its collection. Better yet, users should be able to choose which information is collected in more detail.
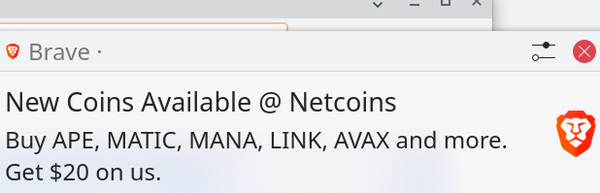
But the biggest contradiction lies in Brave Rewards, which is at the heart of the company’s revenue model. Under Brave Rewards, users can earn cryptocurrency called Basic Attention Tokens (BATs) each month based on the number of targeted ads they choose to view – more information that is promised to be gathered anonymously and can be turned off. Users can also use their Rewards to buy other cryptocurrencies or to tip other sites. The company advertises this system as “privacy-respecting ads” (Figure 7). The problem is that the ads are pop-ups, which are perhaps one of the most distracting forms of ads imaginable. These pop-up ads are no less annoying just because they open in the upper right corner of the window and mostly out of the way. More to the point, the whole point of ad-blocking is to avoid having to engage with ads, and engaging with them more benignly is no less of a nuisance. I can understand the advantage to the company – it shuts out loose ads and creates its own private marketplace. But why should users care, given that the Rewards are minuscule and simply a different kind of intrusion on their privacy?
The Winner in the Conflict
Brave has other limitations. In particular, despite having a dialog for importing bookmarks, bookmarks can only be imported from a .html file under Linux. In addition, Playlist, a feature for the macOS version that collects audio and video, has yet to appear on the Linux version. Such omissions feel like a throwback to the turn of the century, when Linux was treated as a second-class operating system when it was recognized at all. Nothing in Brave compels me to put up with that treatment today.
However, the least appealing feature of Brave is the impression that the company is not really serious about privacy and security. Instead, privacy and security are selling points, and users must simply trust the anonymous company to deal in good faith. Worse, privacy and security are compromised at every turn by the need for profit. Fittingly, the browser’s home page illustrates this conflict neatly: Brave-related material fills most of the open space in the dashboard, and features are crammed into a single line at the bottom right and two icons in the upper left, an arrangement that makes plain which one has priority.
In the end, Brave is simply proof – if any were needed – that the day of the corporate web browser is over, even if it is open source. Although Brave includes features that Chromium and Firefox would benefit from, if you want to ensure privacy and security, turn to the Tor Browser, which gives you the same privacy and security as Brave without any of the corporate compromise.
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
OpenMandriva Lx 6.0 Available for Installation
The latest release of OpenMandriva has arrived with a new kernel, an updated Plasma desktop, and a server edition.
-
TrueNAS 25.04 Arrives with Thousands of Changes
One of the most popular Linux-based NAS solutions has rolled out the latest edition, based on Ubuntu 25.04.
-
Fedora 42 Available with Two New Spins
The latest release from the Fedora Project includes the usual updates, a new kernel, an official KDE Plasma spin, and a new System76 spin.
-
So Long, ArcoLinux
The ArcoLinux distribution is the latest Linux distribution to shut down.
-
What Open Source Pros Look for in a Job Role
Learn what professionals in technical and non-technical roles say is most important when seeking a new position.
-
Asahi Linux Runs into Issues with M4 Support
Due to Apple Silicon changes, the Asahi Linux project is at odds with adding support for the M4 chips.
-
Plasma 6.3.4 Now Available
Although not a major release, Plasma 6.3.4 does fix some bugs and offer a subtle change for the Plasma sidebar.
-
Linux Kernel 6.15 First Release Candidate Now Available
Linux Torvalds has announced that the release candidate for the final release of the Linux 6.15 series is now available.
-
Akamai Will Host kernel.org
The organization dedicated to cloud-based solutions has agreed to host kernel.org to deliver long-term stability for the development team.
-
Linux Kernel 6.14 Released
The latest Linux kernel has arrived with extra Rust support and more.